Given a real number ![]() find the maximum of the function
find the maximum of the function
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[f(E) = \iiint \limits_{E} \left ( \alpha^2 - x^2 - y^2 - z^2 \right )\, \mathrm{d}V\]](https://www.math.tolaso.com.gr/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-af785b7677b97edca385b8dc42916982_l3.png)
where ![]() is any region in space.
is any region in space.
Solution
Let ![]() . Then
. Then
![]()
In the region ![]() we have
we have ![]() hence
hence ![]() which gives
which gives ![]() . Thus ,
. Thus ,
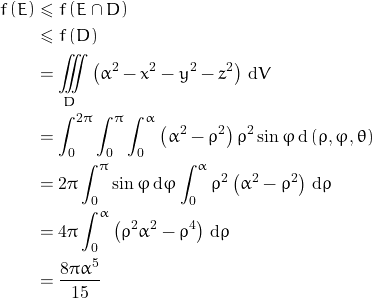
A site of university mathematics
Given a real number ![]() find the maximum of the function
find the maximum of the function
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[f(E) = \iiint \limits_{E} \left ( \alpha^2 - x^2 - y^2 - z^2 \right )\, \mathrm{d}V\]](https://www.math.tolaso.com.gr/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-af785b7677b97edca385b8dc42916982_l3.png)
where ![]() is any region in space.
is any region in space.
Solution
Let ![]() . Then
. Then
![]()
In the region ![]() we have
we have ![]() hence
hence ![]() which gives
which gives ![]() . Thus ,
. Thus ,
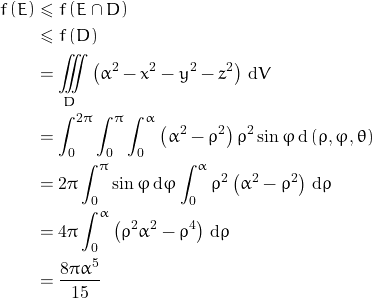
Let ![]() be differentiable on
be differentiable on ![]() and continuous at
and continuous at ![]() . If
. If
![]()
for ![]() then prove that
then prove that ![]() is differentiable at
is differentiable at ![]() .
.
Solution
Let us assume without loss of generality that ![]() . We will show that
. We will show that ![]() as
as ![]() and that means that
and that means that ![]() is differentiable at
is differentiable at ![]() with
with ![]() .
.
Fix ![]() and choose
and choose ![]() such that
such that ![]() ,
, ![]() . Therefore
. Therefore ![]() . Now suppose
. Now suppose ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be the point that coincides with
be the point that coincides with ![]() on the first
on the first ![]() coordinates and is
coordinates and is ![]() elsewhere. Then
elsewhere. Then ![]() is a path from
is a path from ![]() to
to ![]() and each vector
and each vector ![]() is parallel to one of the axes. Hence
is parallel to one of the axes. Hence
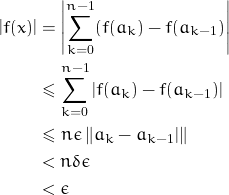
For ![]() we define
we define ![]() and
and ![]() . For which
. For which ![]() does the series
does the series
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\sum_{p=1}^{\infty} \left ( \left \| v \right \|_p - \left \| v \right \|_{\infty} \right)\]](https://www.math.tolaso.com.gr/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-78e15ff882527820bcf3c5130453172c_l3.png)
converge?
Solution ( Robert Tauraso )
We may assume that ![]() is not the zero vector and
is not the zero vector and ![]() otherwise the series is trivially convergent. Then, we show that the series is convergent if and only if there is exactly one component of maximal absolute value.
otherwise the series is trivially convergent. Then, we show that the series is convergent if and only if there is exactly one component of maximal absolute value.
(a) If the above condition is satisfied then, without loss of generality, let ![]() be the component of maximal absolute value and let
be the component of maximal absolute value and let ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \displaystyle t = \frac{\max \limits_{2 \leq i \leq n} \left | x_i \right |}{\left | x_i \right |} \in [0, 1]](https://www.math.tolaso.com.gr/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-881d97458ceaf02cb11cba1de4d0db14_l3.png) . Hence , as
. Hence , as ![]()
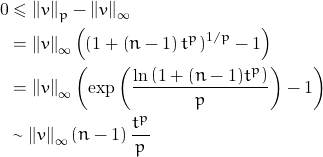
and the given series is convergent because 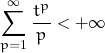 .
.
(b) If the above condition is not satisfied, then there are at least ![]() components of maximal absolute value and therefore
components of maximal absolute value and therefore
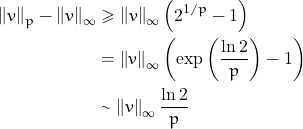
and the given series is not convergent because 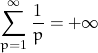 .
.
Let ![]() . Evaluate the integral:
. Evaluate the integral:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathcal{J} = \iint \limits_{\Delta} \arctan e^{xy}\,\mathrm{d}y\,\mathrm{d}x\]](https://www.math.tolaso.com.gr/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ed025cc27a0dfd96e8dbc35ef3cea331_l3.png)
Solution
The key observation to nail the integral is that the domain of integration is symmetric with respect to the ![]() axis.
axis.
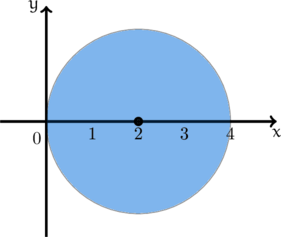
Hence , a symmetry might as well work. So,
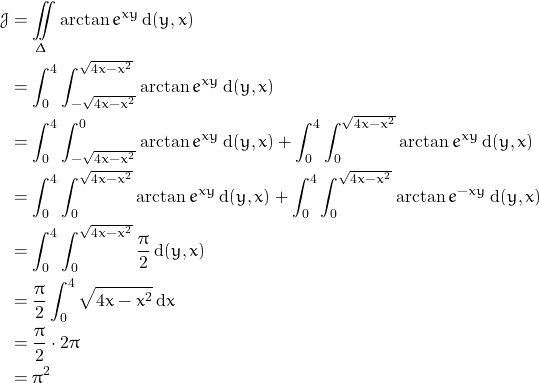
since
![]()
Let ![]() be the volume of the sphere centered at
be the volume of the sphere centered at ![]() and radius
and radius ![]() in
in ![]() . Prove that for
. Prove that for ![]() it holds that
it holds that
![]()
Solution
The volume of the sphere in ![]() is given by:
is given by:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathcal{V}_n (1) = \idotsint \limits_{x_1^2+x_2^2+\cdots+x_n^2 \leq 1} 1 \, \mathrm{d} \left ( x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n \right )\]](https://www.math.tolaso.com.gr/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-df89abfcabbe045680b57b1e0e8ffddc_l3.png)
Parametrize the sphere by
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{matrix} x_1 &= & r \cos \theta_1 \\ x_2 & = & r \sin \theta_1 \cos \theta_2 \\ x_3 & = & r \sin \theta_1 \sin \theta_1 \cos \theta_3 \\ \vdots \\ x_{n-1} & = & r \sin \theta_1 \sin \theta_2 \cdots \sin \theta_{n-2} \cos \theta_{n-1} \\ x_n & = & r \sin \theta_1 \sin \theta_2 \cdots \sin \theta_{n-1} \end{matrix}\]](https://www.math.tolaso.com.gr/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d84a65d63781977f11b9e2b9af2e9ce1_l3.png)
taking
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{matrix} 0 \leq r \leq 1\\ 0 \leq \theta_i \leq \pi & & \text{forall} \;\; i=1, 2, \dots , n-2 \\ 0 \leq \theta_{n-1} < 2 \pi \end{matrix}\]](https://www.math.tolaso.com.gr/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a36931f59fc85fb0cee33bb6f3f88af7_l3.png)
It then follows from the Change of Variables formula that the rectangular volume element ![]() can be written in spherical coordinates as
can be written in spherical coordinates as
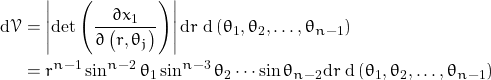
Thus,
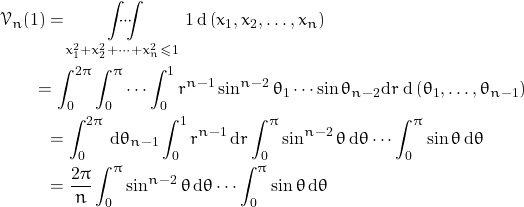
Hence,
(1) ![]()
In particular since ![]() we get that:
we get that:
(2) ![]()
Using ![]() as well as Wallis’ integral we are able to prove the result. Let us assume that
as well as Wallis’ integral we are able to prove the result. Let us assume that ![]() is even, then:
is even, then:
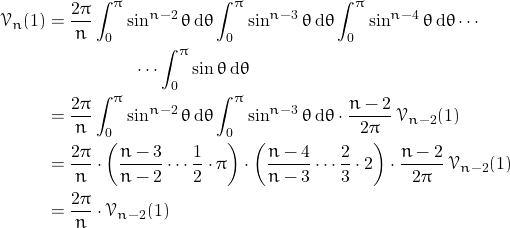
If ![]() is odd we work similarly.
is odd we work similarly.